How Dental Disease Impacts Your Pet’s Overall Health
Dental health is a critical yet often overlooked aspect of pet care. Poor oral hygiene doesn’t just lead to bad breath—it can cause serious health issues affecting multiple organ systems. At Animal Hospital at Hillshore, located in Madison, WI, we are dedicated to educating pet owners about the impact of dental disease on overall pet wellness.
Understanding Dental Disease in Pets
What is Dental Disease?
Dental disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the most common health issues in dogs and cats. It begins with plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth. If left untreated, bacteria from plaque migrate beneath the gum line, causing gum inflammation (gingivitis), infection, tooth decay, and even bone loss.
How Common is Periodontal Disease in Pets?
Studies suggest that by age three, nearly 80% of dogs and 70% of cats show some degree of dental disease. This makes regular oral care an essential part of preventive veterinary medicine.
Stages of Dental Disease
- Stage 1: Gingivitis – Mild inflammation of the gums, often reversible with proper care.
- Stage 2: Early Periodontitis – Infection begins affecting deeper gum tissues; minor bone loss may occur.
- Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis – Increased bone loss, loose teeth, and pain become more apparent.
- Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis – Severe infection leading to tooth loss and potential spread of bacteria to the heart, liver, and kidneys.
Early intervention is key to preventing progression and long-term health complications.
Why Dental Disease Matters: The Connection to Systemic Health
Bacteria in the Bloodstream: A Risk to Major Organs
Oral infections don’t remain isolated in the mouth. When bacteria from the gums enter the bloodstream, they can spread to vital organs, causing serious, life-threatening conditions.
Health Issues Linked to Dental Disease
1. Heart Disease
- Endocarditis, a life-threatening heart valve infection, has been linked to chronic oral bacteria.
- Dogs with periodontal disease are more likely to develop heart murmurs and congestive heart failure.
2. Kidney and Liver Damage
- The kidneys and liver filter bacteria and toxins from the blood.
- Chronic oral infections increase the risk of kidney disease and liver infections, leading to organ failure over time.
3. Chronic Pain and Reduced Quality of Life
- Pets with advanced dental disease may struggle to eat, experience chronic pain, and become lethargic or irritable.
- Weight loss, malnutrition, and behavioral changes are common in pets suffering from severe oral infections.
Ignoring dental care can significantly shorten your pet’s lifespan.
Recognizing the Signs of Dental Disease in Pets
Early detection of dental disease prevents more serious complications.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Bad breath (halitosis) – Persistent foul odor from the mouth.
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums – A sign of inflammation or infection.
- Difficulty eating or chewing – Dropping food, chewing on one side, or avoiding hard food.
- Drooling excessively or pawing at the mouth – Indicates oral pain.
- Loose, broken, or missing teeth – A result of advanced gum disease.
- Visible plaque or tartar buildup – Yellow or brown deposits on the teeth.
- Swelling around the face or jaw – A potential sign of a painful abscess or advanced infection.
If you notice any of these signs, contact Animal Hospital at Hillshore for an evaluation.
Prevention and Treatment: Keeping Your Pet’s Teeth Healthy
1. Routine Veterinary Dental Exams
Regular check-ups allow for early detection of dental disease. Pets should have annual dental exams, and high-risk pets (such as small dog breeds and senior pets) may need more frequent visits.
Schedule your pet’s dental exam today.
2. Professional Dental Cleanings
Even with at-home care, professional cleanings are necessary to remove plaque and tartar below the gumline. These cleanings prevent infection and tooth loss.
At Animal Hospital at Hillshore, we offer comprehensive dental care, including:
- Ultrasonic scaling & polishing
- Dental X-rays to assess hidden issues
- Tooth extractions when necessary
- Post-cleaning oral care plans
3. At-Home Dental Care for Pets
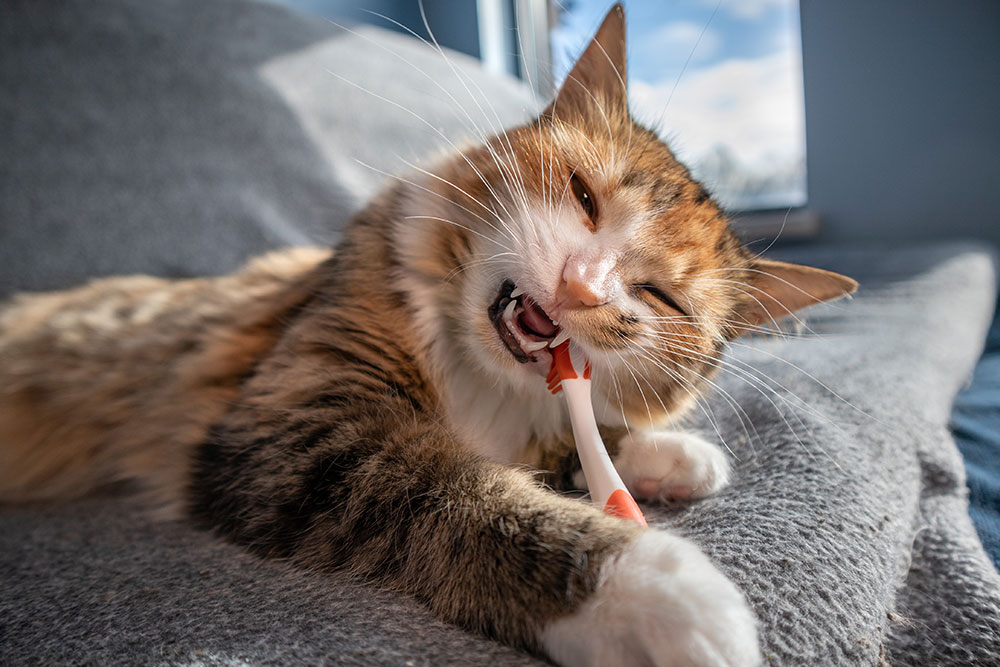
Daily brushing and dental hygiene can significantly reduce plaque buildup.
Recommended at-home care includes:
- Brushing your pet’s teeth daily with pet-safe toothpaste.
- Providing veterinarian-approved dental chews to help reduce tartar.
- Using water additives or dental rinses to combat bacteria.
- Feeding dental-friendly diets formulated to support oral health.
Learn about proper at-home dental care here.
How We Help at Animal Hospital at Hillshore
At Animal Hospital at Hillshore, we offer expert veterinary dental care to keep your pet’s mouth and body healthy. Our wellness and prevention services are designed to detect, prevent, and treat dental disease before it becomes severe.
Why Choose Us?
- Experienced veterinarians dedicated to oral health.
- Advanced technology, including digital dental X-rays.
- Personalized treatment plans for each pet’s needs.
Visit us in Madison, WI, and give your pet the best dental care today.

FAQs About Pet Dental Care
How often should my pet have a dental cleaning?
Most pets benefit from annual cleanings, but frequency depends on breed, age, and individual risk factors.
Is anesthesia necessary for a dental cleaning?
Yes. Anesthesia ensures a thorough, pain-free cleaning and allows for detailed X-rays and deep plaque removal.
Can I use human toothpaste on my pet?
No. Human toothpaste contains toxic ingredients like xylitol. Always use veterinary-approved toothpaste.
Are dental chews and water additives effective?
Yes, but they should supplement, not replace, brushing and professional cleanings.
Take Action: Protect Your Pet’s Oral Health Today
Dental disease is preventable—but only with regular care and veterinary attention. By prioritizing oral hygiene, you can help your pet live a longer, healthier, and pain-free life.
For more information, visit the AVMA’s guide to pet dental care or contact Animal Hospital at Hillshore today.




Leave A Comment